Low water pressure turning your shower into a drizzle?
Frustrated with weak flow from your taps?
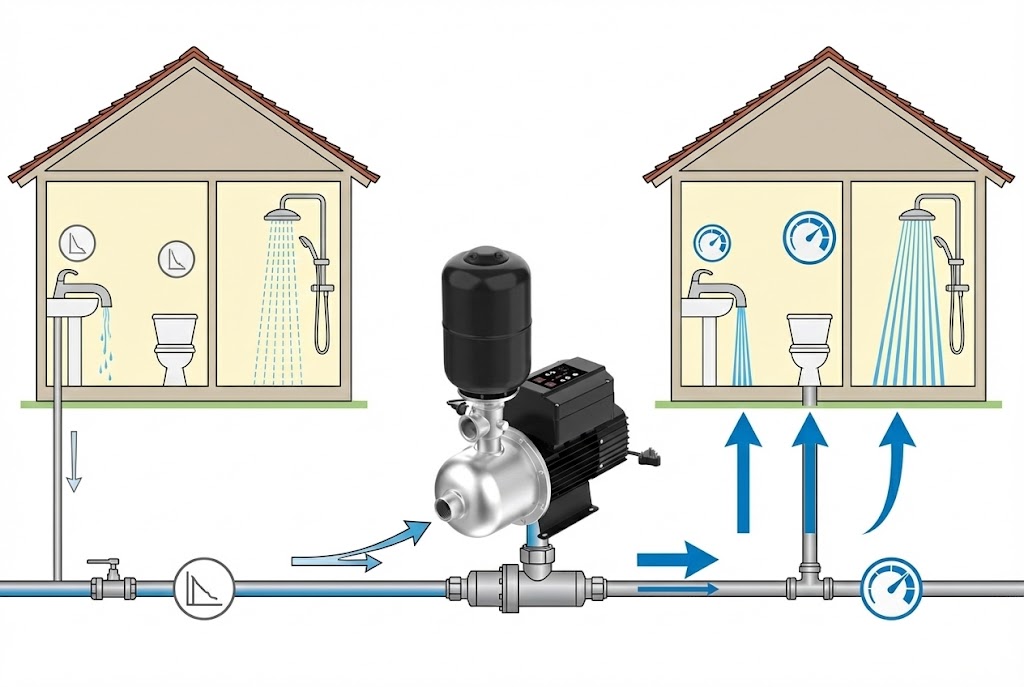
A booster pump can restore powerful, consistent pressure throughout your entire property.
A booster pump increases low water pressure and flow by being installed on your main water supply line.
Correctly diagnosing the issue, selecting a modern pump with the right features, and following proper installation steps are crucial for achieving a reliable, high-performance water system that will last for years.
Struggling with inconsistent water pressure is a common frustration for many property owners.
It can affect everything from daily chores to the performance of appliances.
While a booster pump seems like a straightforward solution, jumping into an installation without proper planning can lead to disappointment, wasted money, or even damage to your plumbing.
The secret to a successful upgrade lies in a methodical approach.
You must first understand the problem, then select the right technology, and finally, ensure a flawless installation.
This guide will walk you through every critical step, from initial diagnosis to post-installation maintenance, ensuring you get the powerful and reliable water pressure you need.
Let's transform your water system from a source of frustration into a model of efficiency.
Before You Install: The Crucial Diagnostic Phase
Rushing to install a pump without understanding the problem can create new issues.
Are you sure a pump is the right solution for your low pressure?
Proper diagnosis is essential.
Before purchasing any equipment, it's critical to measure your existing water pressure and diagnose the true cause of the low flow.
This ensures you select a compatible and effective pump, preventing issues like over-pressurization or unnecessary energy consumption.
Diagnosing the Underlying Problem
The first step is always to play detective.
A booster pump is a solution, but only if low incoming pressure is the actual problem.
Other common culprits can mimic the symptoms of low supply pressure.
Check for partially closed shut-off valves, including the main valve near your water meter and any valves under sinks or behind toilets.
Look for visible leaks in exposed pipes, especially in basements, crawl spaces, or utility closets.
Mineral buildup inside old galvanized steel pipes can severely restrict water flow over time.
If your property is at a high elevation compared to the municipal water main, gravity can naturally reduce the pressure by the time it reaches your fixtures.
A simple pressure gauge test at a spigot closest to the water main can give you a baseline reading to determine if the issue is systemic or localized within your property.
Understanding Modern Pump Technology
Once you've confirmed that a booster pump is necessary, it's vital to choose the right kind.
Oversized pumps can cause water hammer and damage pipes, while undersized pumps will fail to deliver the desired pressure.
Today's market is dominated by intelligent pumps featuring advanced technology that offers significant advantages over older, fixed-speed models.
The core of a modern system is a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) paired with a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD).
This combination allows the pump to adjust its motor speed in real-time to maintain a perfectly stable, constant water pressure, regardless of how many taps are open.
This a stark contrast to older pumps that run at full speed every time they switch on, causing pressure fluctuations and consuming excess energy.
| Feature Comparison | Traditional Pumps | Modern VFD Pumps |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Output | Fluctuates; On/Off cycles | Perfectly constant and stable |
| Energy Use | High; always runs at 100% speed | Very low; up to 50% savings |
| Noise Level | Loud and noticeable | Ultra-quiet (often under 50dB) |
| Motor Start | Abrupt start causes stress | Soft start reduces wear and tear |
| Lifespan | Shorter due to mechanical stress | Longer due to smart operation |
Matching the Pump to Your System's Needs
Determining your required pressure and flow rate is a critical calculation.
Start by listing the fixtures you expect to run simultaneously.
Each fixture has a typical flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM).
Add these up to find your peak demand.
Next, determine the pressure needed.
Most residential fixtures operate well between 40-60 PSI.
The goal is to select a pump that can meet your peak GPM demand while delivering your target PSI.
Advanced VFD pumps offer a wide range of pressure customization, often allowing you to set the output anywhere from 20% to 95% of the pump's maximum capability.
This flexibility ensures you can fine-tune the system perfectly for your specific needs without wasting energy.
Installation Tips for Peak Performance and Longevity
Installing a pump correctly is just as important as choosing the right one.
A poor installation can lead to noise, vibrations, and premature failure.
Want your investment to last?
Following key installation best practices ensures the pump operates efficiently, quietly, and safely for its entire lifespan.
Key steps include using flexible connections, installing a check valve and bypass line, and ensuring secure, dedicated electrical wiring for maximum reliability.
Strategic Placement and Vibration Damping
The location of your pump has a major impact on its effectiveness.
For the best performance, install the pump as close as possible to the main water supply's point of entry into the building, right after the water meter and any main shut-off valve.
This ensures the pump is boosting the pressure for the entire system right from the source.
Vibration is a common side effect of any pump, but it can be easily managed.
Never connect the pump directly to rigid metal pipes.
Instead, use flexible, braided stainless steel connection hoses on both the inlet and outlet ports.
These hoses absorb the pump's vibrations, preventing them from transferring into your home's plumbing system and creating annoying humming or rattling noises.
Mounting the pump on a solid, level surface further reduces operational noise.
Essential Plumbing: Check Valves and Bypass Loops
To control the flow of water and make future maintenance simple, two plumbing components are non-negotiable.
1. The Check Valve:
A check valve, or non-return valve, must be installed on the outlet side of the pump.
This simple device acts as a one-way gate, ensuring that once water is pushed through the pump, it cannot flow backward.
This prevents back pressure against the pump's impeller when it shuts off and stops the system from losing pressure.
2. The Bypass Loop:
A bypass loop is a professional touch that saves major headaches down the road.
It consists of a separate pipe that runs parallel to the pump, with three shut-off valves:
- One on the inlet pipe before the pump.
- One on the outlet pipe after the pump.
- One on the bypass pipe itself.
During normal operation, the inlet and outlet valves are open, and the bypass valve is closed.
If the pump ever needs maintenance, you can simply close the inlet and outlet valves and open the bypass valve.
This isolates the pump completely while allowing water from the municipal supply to continue flowing to your home, ensuring you're never without water.
Ensuring Electrical Safety and Reliability
A booster pump is a powerful electrical appliance that requires a safe and stable power source.
It should always be powered by a dedicated circuit with its own breaker at the electrical panel.
This prevents the pump from overloading a shared circuit, which could trip the breaker and affect other appliances.
Modern VFD pumps are often designed with excellent power grid adaptability, able to function perfectly across a wide voltage range (e.g., 165V to 260V).
This makes them highly reliable even in areas with unstable electrical grids.
The electronic components, however, are sensitive.
High-end pumps feature fully sealed PCB controllers with a potting compound.
This creates a 100% waterproof and dustproof seal, often achieving an IP67 rating, which protects the electronics from moisture and condensation—the leading cause of electronic failure in pumps.
This single feature can extend the controller's life by several years.
After Installation: System Protection and Maintenance
Your new pump is installed, but the job isn't finished.
How can you ensure it runs flawlessly for the next decade?
Proper system protection and regular maintenance are key.
After installation, it's crucial to check for proper water flow before powering up the unit.
Following a simple maintenance schedule and understanding the pump's built-in protection features will guarantee consistent performance, efficiency, and a long operational life.
The Importance of the Initial Power-Up
Before you flip the switch for the first time, you must prime the pump.
Never run a booster pump dry.
Operating without water, even for a few seconds, can generate immense heat from friction and destroy the internal seals and impeller.
To prime the pump, ensure all valves are in their correct operating positions and slowly open the inlet valve.
Let water flow completely through the pump and into the plumbing system.
You should be able to hear the water filling the pump casing and pipes.
Once you are certain the pump is full of water, you can safely connect it to power and turn it on.
Understanding Intelligent System Protections
The true value of a modern VFD booster pump lies in its intelligence.
These units are equipped with a sophisticated suite of self-preservation functions that actively monitor and protect the system from damage.
A premium pump may feature as many as 14 distinct safety shields.
Key built-in protections to look for include:
- Dry Run Protection: If the pump detects a water shortage, it won't burn itself out. Instead, it initiates a smart recovery algorithm. It will stop, wait for a set period (e.g., 5 minutes), and then attempt to self-prime again. If the water shortage persists, it will progressively lengthen the waiting period to conserve energy while periodically checking for water return.
- Thermal and Electrical Protection: The system constantly monitors for input voltage that is too high or too low, overcurrent situations, and overheating of the motor or driver board, shutting down safely before damage can occur.
- Antifreeze Protection: In cold climates, the pump can automatically run for a few moments if the water temperature drops near freezing, preventing ice from forming and cracking the pump casing.
- Leak Warning: By monitoring pressure patterns, the pump can even detect small, persistent leaks in your plumbing system and alert you to the problem.
Performing Routine Maintenance
While modern pumps are designed to be low-maintenance, a few simple checks will ensure they continue to operate at peak efficiency for years to come.
Set a biannual reminder to perform the following:
- Clean Inlet Screens: Most pumps have a small filter or screen on the inlet side. Check and clean this to ensure no sediment or debris is restricting flow into the pump.
- Check for Leaks: Visually inspect all connections around the pump and the bypass loop for any signs of weeping or drips.
- Verify Pressure Tank Charge: The small pressure tank attached to the system helps reduce pump cycling and absorb water hammer. Use a tire pressure gauge to check that the air pressure inside the tank matches the manufacturer's specification (usually checked when the system is drained). A properly charged tank can reduce pump start/stop cycles by up to 70%, dramatically extending motor life.
- Monitor Performance: Many VFD pumps have a digital display that can show real-time operating data, such as power consumption, motor speed (RPM), and internal temperatures. Periodically cycling through these readings can give you valuable insight into the health of your system.
Conclusion
Properly installing a quality booster pump transforms your water system.
By diagnosing the issue, choosing the right VFD technology, and following key installation and maintenance steps, you guarantee a powerful, reliable, and efficient water supply.
FAQs
What is the best location to install a water booster pump?
Install it horizontally on the main water line, just after the water meter and main shut-off valve, to boost pressure for the entire property effectively.
Can a booster pump be too powerful?
Yes. An oversized pump can create excessively high pressure (over 80 PSI), which can damage pipes, fittings, and appliances. Proper sizing is crucial.
Do I need a pressure tank with a VFD booster pump?
Yes, a small pressure tank is highly recommended. It absorbs pressure spikes, reduces pump cycling for small water uses, and extends the motor's lifespan.
How do I know if my water pressure is low?
Use a pressure gauge on an outdoor hose bibb. Consistent readings below 40 PSI typically indicate low pressure that could benefit from a booster pump.
Can a booster pump pull water from a well?
Some self-priming booster pumps can pull water from shallow wells or storage tanks, but deep wells require a dedicated submersible well pump.
How much electricity does a booster pump use?
Modern VFD booster pumps are very efficient, using up to 50% less energy than older models by only running at the speed needed to maintain pressure.
Are booster pumps noisy?
Older pumps can be loud. However, modern VFD pumps with permanent magnet motors are designed for ultra-quiet operation, often running at noise levels below 50 decibels.








